MMO Coated Titanium Anodes vs Traditional Anodes: Complete Comparison

- Introduction: The Critical Function of Anodes in Electrochemical Processes
- Defining Traditional Anodes: Limitations of Graphite, Lead Dioxide, and Platinum
- What is MMO? Understanding the Technology of Mixed Metal Oxide Coated Titanium Anodes
- Performance Comparison: Service Life, Current Density, and Efficiency
- Corrosion Resistance and Stability in Diverse Electrolyte Environments
- Economic Analysis: Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and Operating Expenses
- Optimal Applications and Selection Criteria for MMO vs. Traditional Anodes
- Future Trends: Innovation in Anode Coatings and Electrochemical Solutions
Introduction: The Critical Function of Anodes in Electrochemical Processes
The anode serves as the operational heart of any electrochemical system, dictating the overall efficiency, energy consumption, and long-term stability of processes ranging from metal recovery and electroplating to chlor-alkali production and environmental water treatment.
In simple terms, the anode is the electrode where the oxidation reaction occurs, driving the required chemical conversion. Its performance characteristics—including catalytic activity, corrosion resistance, and overpotential—are non-negotiable factors for industrial viability. Choosing the correct anode material is often the single most critical engineering decision, directly impacting the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) of the electrolytic cell.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Industrial Anodes:
- Service Life: The duration until the anode coating or substrate degrades to an unacceptable level, necessitating replacement.
- Electrocatalytic Activity: The efficiency with which the anode facilitates the target oxidation reaction (e.g., oxygen evolution, chlorine evolution) at minimal energy input (low overpotential).
- Dimensional Stability: The ability to maintain shape and structure over prolonged use, ensuring consistent electrode gap and system geometry. Traditional anodes often suffer from structural breakdown, which MMO anodes are designed to prevent.
This comparison guide will provide technical procurement managers and electrolysis engineers with a data-driven analysis of how modern Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) coated titanium anodes fundamentally outperform and displace traditional anode materials in demanding industrial applications.
Defining Traditional Anodes: Limitations of Graphite, Lead Dioxide, and Platinum
Before the widespread adoption of dimensionally stable anodes (DSAs), electrochemical industries relied on materials that, while cheap or historically proven, suffered from severe operational and maintenance drawbacks. Understanding these limitations is crucial for justifying the shift to modern coated titanium systems.

Graphite Anodes: High Consumption and Dimensional Instability
Graphite anodes are characterized by their low initial cost. However, they are chemically consumed during electrolysis, especially in aggressive environments like chlor-alkali production. This consumption leads to two major issues:
- High Replacement Rate: The anode requires frequent replacement, significantly increasing maintenance downtime and operational expense.
- Changing Electrode Gap: As the anode dissolves (or is consumed), the distance between the anode and cathode changes. This fluctuating gap leads to inconsistent current distribution, varying cell voltage, and decreased energy efficiency.
Lead Dioxide (PbO2) Anodes: Toxicity and Low Overpotential
Lead dioxide anodes are still utilized in some specialized applications, particularly those requiring high oxygen evolution overpotential. However, their major disadvantages center on environmental and structural instability:
- Environmental and Health Risks: The use of lead-based materials introduces significant toxicity and disposal challenges, necessitating stringent regulatory compliance.
- Sludge Formation: PbO2 coatings can degrade, leading to the formation of lead sludge (PbO), which contaminates the electrolyte and often requires costly purification steps.
- Low Current Density Capacity: These anodes are typically limited in the current density they can sustain compared to MMOs before severe degradation occurs.
Platinum Anodes: High Cost and Passive Surface
Platinum (Pt) anodes offer excellent corrosion resistance and good catalytic activity, but their prohibitive material cost makes them economically unviable for large-scale industrial processes unless the application is highly specialized or involves low current densities. Furthermore, the catalytic layer is extremely thin and can be passivated or physically damaged, leading to premature failure.
The Critical Issue: Dimensional Stability
Traditional anodes are fundamentally Non-Dimensionally Stable. This lack of stability (due to consumption or structural breakdown) necessitates constant operational adjustments, undermines process quality, and drives up the energy consumption required to overcome the growing resistance.
What is MMO? Understanding the Technology of Mixed Metal Oxide Coated Titanium Anodes
Mixed Metal Oxide (MMO) coated titanium anodes represent a fundamental technological leap, solving the dimensional instability and operational constraints associated with traditional anode materials. These anodes are often referred to as Dimensionally Stable Anodes (DSAs).
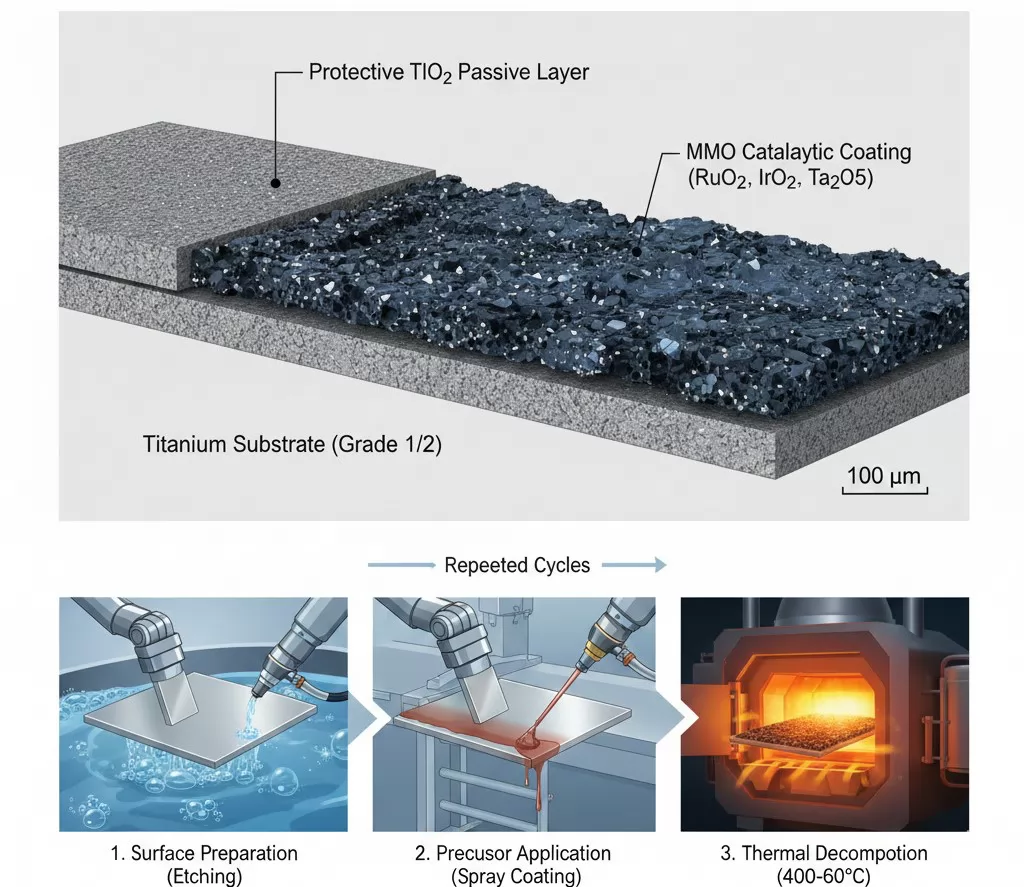
The Core Structure: Titanium Substrate
The foundation of an MMO anode is a titanium substrate (usually Grade 1 or Grade 2). Titanium is selected not for its catalytic properties, but for its exceptional corrosion resistance and ability to passivate—forming a protective oxide layer that makes it nearly inert in most aggressive electrolyte environments. Crucially, titanium allows the anode to maintain a stable form throughout its service life.
The Active Layer: Mixed Metal Oxides
The catalytic activity resides in the coating, which consists of a mixture of precious metal oxides, such as RuO2 (Ruthenium Dioxide), IrO2 (Iridium Dioxide), and Ta2O5 (Tantalum Pentoxide). The exact composition is proprietary and specifically engineered for the target application:
- Ruthenium-Iridium (RuO2/IrO2): Highly efficient for chlorine evolution reactions (C.E.R.), commonly used in chlor-alkali and hypochlorite generation.
- Iridium-Tantalum (IrO2/Ta2O5): Superior stability for oxygen evolution reactions (O.E.R.) in highly acidic or oxygen-rich environments, typical in copper electrowinning or sewage treatment.
- Platinum-Iridium (Pt-Ir): Used where extremely high purity is required, combining the stability of Ir with the established electrocatalysis of Pt.
The Manufacturing Process
The performance of the MMO coating is highly dependent on the manufacturing process:
Key Manufacturing Steps (Thermal Decomposition):
- Surface Preparation: The titanium substrate is mechanically and chemically etched to create a rough, clean surface for optimal adhesion.
- Precursor Application: Liquid precursors of the noble metals are applied to the substrate (e.g., via brush, dip, or spray coating).
- Thermal Decomposition: The coated substrate is heated to high temperatures (typically 400°C to 600°C). This thermal treatment decomposes the metal salts into their respective stable, crystalline oxide forms (MMO). This process is repeated multiple times to achieve the required coating thickness and homogeneity.
The resulting MMO coating is highly adherent, electrically conductive, and chemically stable, allowing the anode to maintain exceptional catalytic activity over thousands of operating hours.
Performance Comparison: Service Life, Current Density, and Efficiency
The definitive advantage of MMO coated titanium anodes lies in their superior electrochemical performance metrics, which translate directly into lower operational expenditure (OpEx) and higher throughput capacity compared to traditional materials.
1. Extremely Low Overpotential
Overpotential (eta) is the excess voltage required beyond the theoretical reversible potential to drive an electrochemical reaction. MMO coatings, due to their specific crystalline structure and high surface area, act as highly efficient electrocatalysts. This significantly reduces the operating voltage of the cell:
- MMO Anodes: Typically operate with a low eta. For example, RuO2/IrO2 coatings for chlorine evolution can save 300 mV to 500 mV compared to graphite or lead electrodes.
- Impact: A reduction in voltage directly decreases the energy consumption (E = V times I times t). In high-current applications, this results in massive, sustained energy savings over the anode's lifespan.
2. High Current Density Capacity
MMO anodes are designed to operate efficiently under high current densities (A/m^2). The robust and non-consumable titanium substrate, combined with the stable, conductive oxide coating, allows for higher production rates without risk of premature failure or passivation that plagues materials like lead dioxide or graphite.
This allows engineers to design more compact and high-throughput electrolytic cells, optimizing factory floor space and capital expenditure (CapEx).
3. Exceptional Service Life (Durability)
While traditional anodes degrade and dissolve, MMO anodes are only subject to a very slow rate of "coating wear," mainly due to minor dissolution or detachment caused by prolonged oxygen or chlorine evolution. The service life is significantly extended:
- Traditional Anodes: Service life often measured in months (e.g., graphite, PbO2).
- MMO Anodes: Service life is typically measured in years (e.g., 3 to 10 years, depending on current density and electrolyte). Once the coating is depleted, the substrate can often be recoated (refurbished), further improving sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
| Performance Metric | MMO Coated Titanium Anodes | Traditional Anodes (Graphite/PbO2) |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent (DSA): Maintained geometric shape. | Poor: Subject to consumption and structural change. |
| Operating Overpotential | Low: High catalytic activity ensures energy efficiency. | High: Drives up energy consumption. |
| Current Density Limit | High: Suitable for high-throughput systems. | Low: Limits production capacity. |
| Recyclability/Refurbishment | High: Titanium substrate can be recoated. | Low: Consumed material must be discarded. |
Corrosion Resistance and Stability in Diverse Electrolyte Environments
A major determinant of anode longevity is its ability to withstand chemical attack in aggressive and varied electrolyte solutions. MMO coated titanium anodes exhibit superior resistance characteristics compared to their traditional counterparts.

Titanium: The Ideal Substrate
The corrosion immunity of the MMO anode starts with the titanium substrate. Titanium naturally forms a passive, thin, and protective oxide layer when exposed to water or oxygen. If the MMO coating is locally damaged, the underlying titanium instantly repassivates, preventing galvanic corrosion or dissolution of the substrate. This characteristic is particularly vital in:
- High Chloride Concentrations: Where lead and graphite suffer rapid breakdown.
- Acidic Solutions (pH < 4): Where the titanium substrate maintains structural integrity, even when traditional materials may fail.
The Stability of Mixed Metal Oxides (RuO2/IrO2)
The specific selection of mixed metal oxides provides tailored chemical stability. For instance:
- Iridium Oxide (IrO2): Essential for applications involving Oxygen Evolution Reactions (OER), especially in highly acidic media (e.g., sulfuric acid-based electrowinning). IrO2 is one of the most stable catalytic oxides under these aggressive oxidizing conditions.
- Ruthenium Oxide (RuO2): Highly stable and catalytic for Chlorine Evolution Reactions (CER) in brine solutions, minimizing the undesirable side reaction of oxygen evolution.
Case Study: Reverse Polarity and Cell Shutdown
Industrial processes often require brief periods of reverse polarity or suffer unexpected cell shutdowns. During these events, traditional anodes are highly susceptible to chemical damage:
- Traditional Anodes: Graphite swells and crumbles. Lead dioxide coatings crack or detach.
- MMO Anodes: The titanium substrate provides inherent tolerance to voltage reversal (short-term) and the non-consumable nature of the oxides means they are less affected by rapid changes in potential or electrolyte chemistry during unexpected shutdowns. The DSA structure maintains its physical and chemical stability, allowing for quicker and smoother system restarts.
This enhanced stability reduces maintenance costs and critical process interruptions, directly supporting the principles of reliable, continuous industrial operation.
Economic Analysis: Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and Operating Expenses
While the initial capital expenditure (CapEx) for MMO coated titanium anodes may be higher than for traditional materials like graphite or lead, a thorough Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis overwhelmingly favors MMO technology due to significant reductions in operational expenses (OpEx).
1. Energy Savings: The Dominant Factor
As established, the low overpotential of MMO coatings is the single greatest economic advantage. The energy consumed in electrolysis is proportional to the cell voltage. Over a 3-5 year lifespan, the cumulative savings from operating at a lower voltage (e.g., 300 mV less per cell) dwarf the initial material cost difference. For high-volume production facilities, this translates to hundreds of thousands of dollars saved annually.
2. Reduced Maintenance and Downtime
Traditional anodes, being consumable or dimensionally unstable, require frequent replacement, which necessitates:
- High Labor Costs: For cell disassembly, cleaning, and reinstallation.
- Lost Production Time: Downtime means zero output and lost revenue.
MMO anodes, with service lives often exceeding three years before recoating, dramatically minimize maintenance cycles, leading to higher operational reliability and uptime.
3. Recoatability and Extended Asset Life
The core titanium substrate is a highly valuable, long-term asset. When the MMO active coating eventually depletes, the substrate can be returned to the manufacturer (like JH) for chemical stripping and re-coating. This process:
- Significantly reduces the cost of anode replacement (as the titanium metal is reused).
- Minimizes waste and aligns with sustainable industrial practices.
TCO Calculation Summary: MMO vs. Traditional
The TCO calculation for an electrolytic system must balance CapEx and OpEx:
- CapEx: MMO Anode Cost + Electrolytic Cell Cost.
- OpEx: Energy Cost + Maintenance/Downtime Cost + Replacement Cost.
MMO technology lowers the OpEx so drastically through energy savings and reduced maintenance that the payback period for the initial investment is typically short, making them the most cost-effective solution over the life of the plant.
Optimal Applications and Selection Criteria for MMO vs. Traditional Anodes
The choice between MMO and traditional anodes is not arbitrary; it depends critically on the specific operating conditions, the required electrochemical reaction, and the economic goals of the facility.

MMO Anodes: Where High Performance is Mandatory
MMO coated titanium anodes are the superior choice when the primary requirements are high current density, long operational life, energy efficiency, and high product purity. They dominate the following key industrial sectors:
1. Chlor-Alkali Industry
Reaction: Chlorine Evolution Reaction (CER).Coating Type: RuO2/IrO2 based coatings.Advantage: DSAs replaced graphite in this sector, eliminating dimensional changes and achieving massive energy savings while maintaining consistent, high-purity chlorine and caustic soda production.
2. Water Treatment (Electrodeionization, Seawater Electrolysis)
Reaction: Oxygen and Chlorine Evolution.Coating Type: Often Iridium-based for OER stability.Advantage: The stability and inert nature of titanium are crucial in treating challenging, variable water compositions (e.g., wastewater, brine), ensuring the anode does not contaminate the treated water.
3. Metal Electrowinning and Electroplating
Reaction: Oxygen Evolution (OER) in highly acidic solutions.Coating Type: IrO2/Ta2O5 coatings.Advantage: Offers the necessary stability in hot, corrosive sulfuric acid baths (e.g., copper, nickel electrowinning) where lead dioxide electrodes historically failed or caused toxic contamination.
Traditional Anodes: Limited Scope
Traditional anodes are now typically confined to niche or legacy applications where initial CapEx is prioritized over long-term OpEx, or where the electrolyte specifically prohibits the use of titanium (which is rare).
- Graphite: Used in some legacy molten salt systems or low-current, non-critical chemical processes.
- Lead Dioxide: Restricted to specific plating baths or oxidizing environments where the unique high OER overpotential is intentionally desired.
Selection Criteria for Engineers
When selecting an anode, technical managers must evaluate:
- Electrolyte Chemistry: Is it highly acidic, brine, or alkaline? (Determines the required MMO blend).
- Target Current Density: Low, medium, or high? (High density mandates MMO).
- Economic Horizon: Short-term CapEx vs. Long-term TCO.
- Environmental/Purity Requirement: Is the process sensitive to lead or carbon contamination? (MMO guarantees cleanliness).
Future Trends: Innovation in Anode Coatings and Electrochemical Solutions
The field of electrochemical materials is continuously evolving, driven by the global imperative for energy efficiency, decarbonization, and increasingly stringent environmental standards. MMO coated titanium anodes are at the forefront of this innovation.

1. Focus on Low-Energy Evolution Reactions
Future R&D is highly focused on optimizing the coating microstructure and composition to further lower the overpotential, particularly for the two most common reactions:
- Enhanced OER Catalysts: Development of highly stable, cost-effective Ir-based or novel non-precious metal oxide coatings that perform efficiently in highly oxidizing environments for applications like clean energy production.
- Advanced CER Catalysts: Refining the Ru-based coatings to achieve near-theoretical limits of chlorine evolution efficiency, minimizing the undesirable side product of oxygen evolution.
2. Green Hydrogen Production
The massive expansion of green hydrogen production via water electrolysis (both PEM and Alkaline) is a major driver for anode technology. This application demands extremely durable and efficient MMO anodes, particularly those engineered for low oxygen and hydrogen evolution overpotential. The demand here is pushing manufacturers to develop large-format, high-current density DSAs that can withstand high pressures and temperatures.
3. Integration into Customized Electrolytic Systems
The trend is moving away from simply supplying an anode as a component and towards delivering integrated electrochemical solutions. This involves designing the anode shape, the electrolytic cell structure, and the power system as a cohesive unit to maximize process efficiency. Customization includes:
- Complex Shapes: Utilizing titanium's formability to create mesh, tube, or specialized plate geometries for optimized surface area in flow reactors.
- Complete Technical Systems: Offering the anode as part of a complete solution for processes like hypochlorite generation or electrocoagulation.
The Role of Material Science in Sustainability
By extending service life and facilitating the refurbishment of the substrate, MMO technology inherently promotes sustainability compared to the disposable nature of traditional anodes. Continuous innovation in coating processes aims to further increase the lifespan per gram of precious metal used, driving down both cost and environmental impact.
The shift from traditional consumable materials to robust, engineered MMO coated titanium DSAs is a non-reversible path, driven by superior economic performance and operational reliability.
Company Introduction: Shaanxi Jinhan Rare Precious Metal Co., Ltd. (JH)
Located in Baoji, the “China Titanium Valley,” Shaanxi Jinhan Rare Precious Metal Co., Ltd. (JH) specializes in the R&D, production, and global export of high-performance titanium anodes and electrochemical materials.
With a foundation established in 2009, JH brings over a decade of focused experience in developing Dimensionally Stable Anodes (DSA). Our product portfolio includes highly specialized coatings—including ruthenium-iridium, iridium-tantalum, platinum, and lead dioxide—for diverse applications in electroplating, water treatment, and green hydrogen production.
Key Facts & Capabilities
- Established in 2009: More than a decade of expertise in anode development.
- Global Exporter: Over 80% of our production is exported worldwide, serving 300+ customers.
- Annual Sales: Exceeding 8,000,000, demonstrating strong market trust.
- Skilled Team: A dedicated team of 60+ professionals ensuring strict quality control and continuous innovation.
Why Choose JH Anodes: Solution-Driven Performance
We are committed to transitioning from a product supplier to a comprehensive solution provider. Our value proposition is based on tangible engineering benefits, not just materials supply:
- Engineered Longevity: Continuous investment in R&D innovation focused on improving the corrosion resistance and service life of anode coatings, guaranteeing the lowest TCO for our clients.
- Customized Electrolytic Systems: We don't just supply anodes; we design customized electrolytic cells and complete technical systems tailored to your specific chemical environment and process requirements, maximizing electrolysis efficiency.
- Strict Quality Control: From titanium substrate preparation to final thermal decomposition, our quality management ensures every anode meets the demanding standards of the global industrial market.
Contact Our Engineering Team
For complex industrial electrolysis projects, the correct anode selection is critical. Do not rely on off-the-shelf solutions. Contact our engineering and R&D team today to discuss your specific electrolyte chemistry, current density requirements, and service life goals.
Optimize your process efficiency and reduce operational costs with a custom-engineered MMO anode solution from JH.
-
 Oct 29, 2025What is a Titanium Anode (Complete Guide)
Oct 29, 2025What is a Titanium Anode (Complete Guide) -
 Dec 19, 2025Titanium Anode Lifespan Testing: How to Accurately Predict Service Life
Dec 19, 2025Titanium Anode Lifespan Testing: How to Accurately Predict Service Life -
 Dec 25, 2025Titanium Anodes vs Graphite Anodes: Service Life and Cost Analysis
Dec 25, 2025Titanium Anodes vs Graphite Anodes: Service Life and Cost Analysis -
 Dec 17, 2025MMO Coated Titanium Anodes vs Traditional Anodes: Complete Comparison
Dec 17, 2025MMO Coated Titanium Anodes vs Traditional Anodes: Complete Comparison
-
 Jan 22, 2026PCB Circuit Board Plating: Titanium Anode Applications in Practice
Jan 22, 2026PCB Circuit Board Plating: Titanium Anode Applications in Practice -
 Jan 13, 2026Automotive Parts Plating: How Titanium Anodes Significantly Enhance Coating Quality and Performance
Jan 13, 2026Automotive Parts Plating: How Titanium Anodes Significantly Enhance Coating Quality and Performance -
 Jan 05, 2026Electrochemical Solutions for Hospital Wastewater Treatment
Jan 05, 2026Electrochemical Solutions for Hospital Wastewater Treatment -
 Dec 25, 2025Titanium Anodes vs Graphite Anodes: Service Life and Cost Analysis
Dec 25, 2025Titanium Anodes vs Graphite Anodes: Service Life and Cost Analysis
